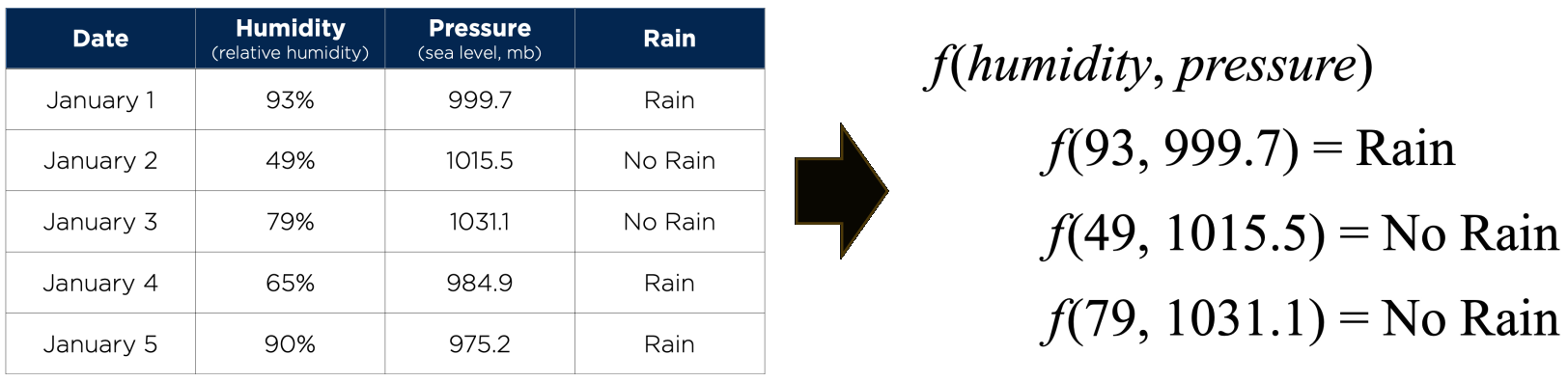
Agent가 세상을 관찰한 후 성능을 향상시키면 학습하는 것 Agent가 컴퓨터일 때 machine learning이라 부름: 컴퓨터가 data를 관찰하고, data 기반 model을 구축하며, 이 model을 세상에 대한 가설이자 문제 해결 software로 사용 Machine이 학습해야 하는 이유 설계자(프로그래머)가 모든 가능한 미래 상황을 예측할 수 없음 설계자가 해결책을 program하는 방법을 모르는 경우 대부분의 사람들은 가족 얼굴 인식에 능숙하지만, 무의식적으로 수행 본 과정에서는 다양한 machine learning model (알고리즘)을 탐색 Input과 함께 제공되는 세 가지 type의 feedback이 있으며, 이는 세 가지 주요 학습 type을 결정 Supervised learning: Agent가 input-output 쌍을 관찰하고 input에서 output으로 mapping하는 함수를 학습 예: camera 이미지(input)와 "버스", "보행자" 등(output)의 쌍 이러한 output을 label이라고 함 Agent는 새로운 이미지가 주어졌을 때 적절한 label을 예측하는 함수를 학습
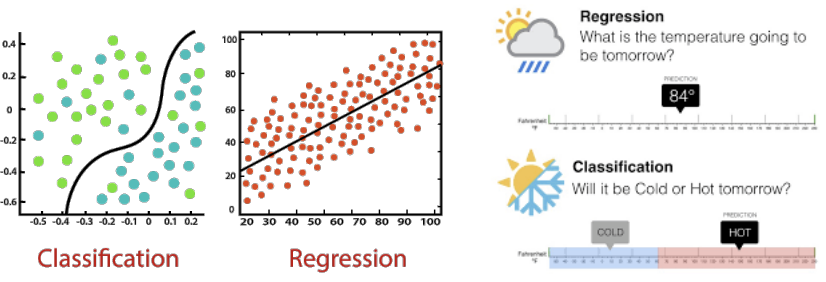
Output이 유한한 값 집합(예: sunny / cloudy / rainy 또는 true / false) 중 하나일 때, 학습 알고리즘을 classification이라 함 Output이 숫자(예: 내일의 기온)일 때, 학습 알고리즘은 regression이라 불림
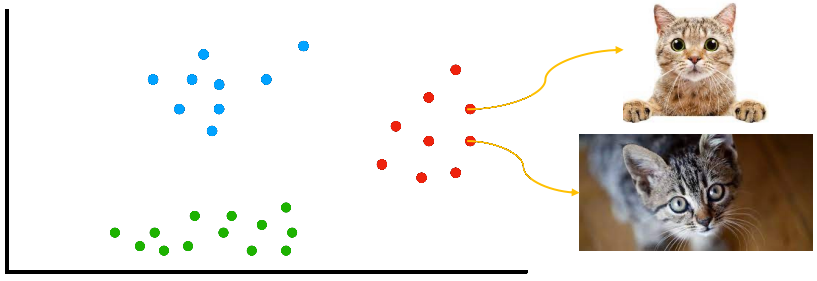
Unsupervised learning: Agent가 명시적인 feedback 없이 input의 pattern을 학습 가장 일반적인 unsupervised learning task는 clustering 잠재적으로 유용한 input example의 cluster 감지 예: Internet에서 가져온 수백만 개의 이미지를 보고, computer vision system이 영어 사용자가 "cats"라고 부르는 유사한 이미지의 큰 cluster를 식별
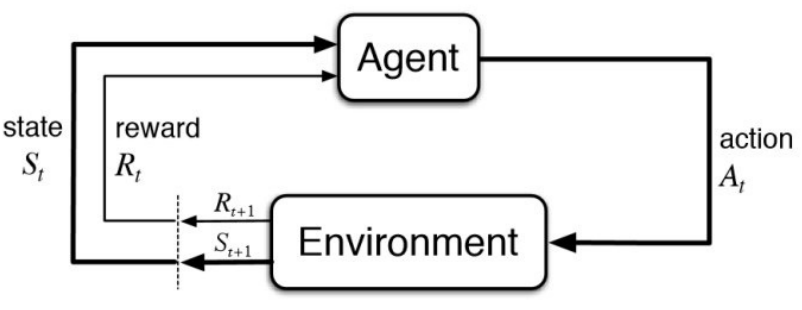
Reinforcement learning: Agent가 일련의 reinforcement (보상 및 처벌)로부터 학습 예: Chess 게임이 끝난 후 agent는 이겼음(보상) 또는 졌음(처벌)을 통보받음 Reinforcement 이전에 어떤 action이 가장 책임이 있는지 결정하고, 미래에 더 많은 보상을 목표로 action을 변경하는 것은 agent의 몫
Reinforcement learning Supervised learning Reinforcement learning은 순차적으로 결정을 내리는 것. 간단히 말해, output은 현재 input의 상태에 따라 달라지며 다음 input은 이전 output에 따라 달라진다고 말할 수 있음. Supervised learning에서는, 결정이 초기 input 또는 처음에 주어진 input에 따라 내려짐. Reinforcement learning에서 결정은 종속적이므로, 종속적인 결정의 sequence에 label을 부여 Supervised learning에서 결정은 서로 독립적이므로, 각 결정에 label이 주어짐. 예: Chess game 예: Object recognition
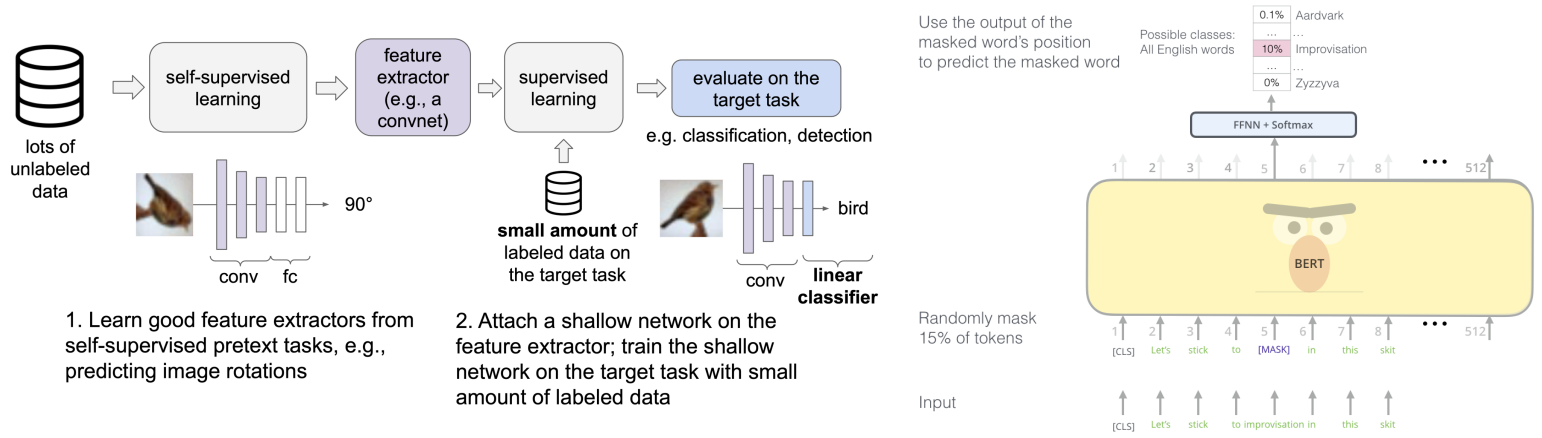
이전 세 가지 범주화 측면에서 unsupervised learning에 속함 Self-supervised learning (SSL) method는 downstream task에 좋은 feature를 생성하는 "pretext" task를 해결 Pretext: 구실, 핑계 Supervised learning objective (예: classification, regression)로 학습 이러한 pretext task의 label은 자동으로 생성됨 예: 이미지 변형 예측 학습 / 손상된 이미지 완성 학습 SSL의 강점 Pretext task 해결을 통해 model이 좋은 feature를 학습 가능 Pretext task를 위한 label을 자동으로 생성 가능 SSL의 의미 일반적으로 self-supervised learning task의 성능에는 관심이 없음 (예: model이 이미지 회전 예측을 완벽하게 학습하는지 여부는 중요하지 않음) 학습된 feature encoder를 downstream target task에서 평가
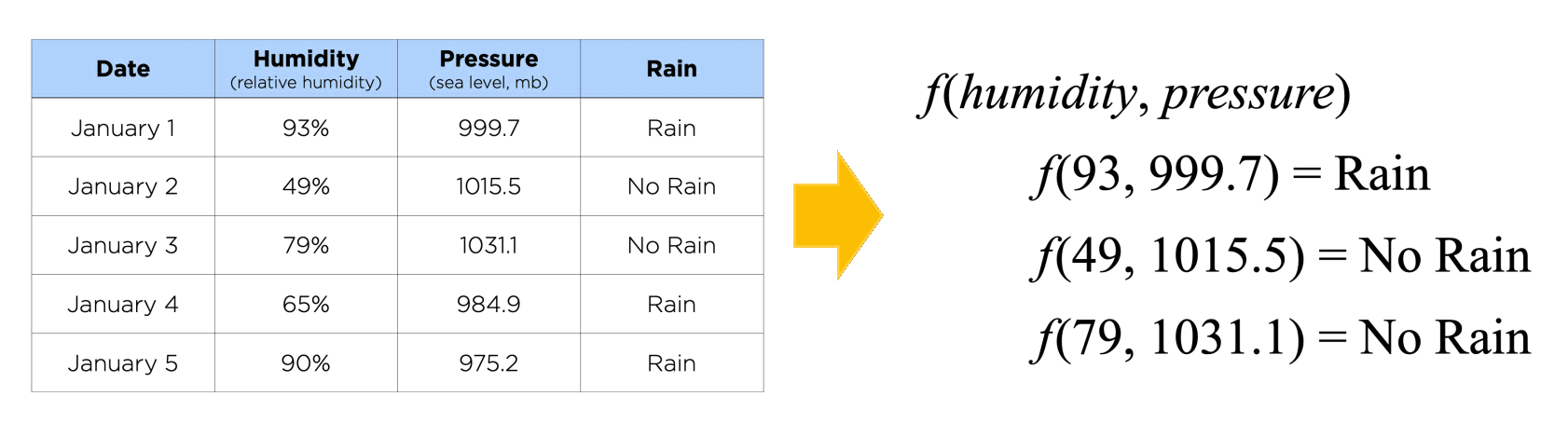
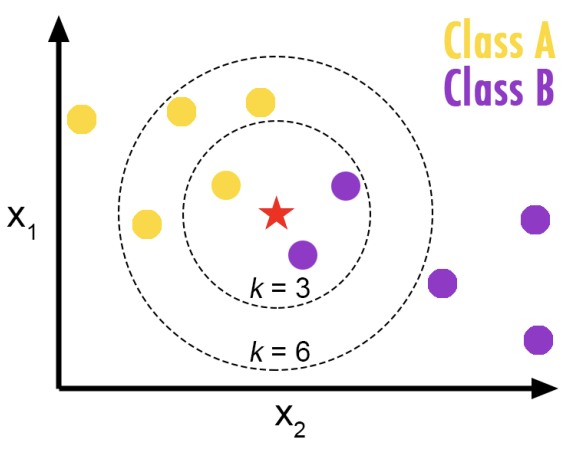
Supervised learning: Input-output 쌍의 data set이 주어지면, input을 output에 mapping하는 함수를 학습 Classification: Input point를 discrete category로 mapping하는 함수를 학습하는 supervised learning task Nearest-neighbor classification: Input이 주어지면, 해당 input에서 가장 가까운 data point의 class를 선택하는 알고리즘 k k k k k k k k k k k k Input: Data set에서 k k k Training example은 일반적으로 다차원 feature space의 vector이며, 각각 class label을 가짐 Output k k k k k k k k k 강점 Training이 (거의) 필요 없음: 알고리즘의 training phase는 training sample의 feature vector와 class label을 저장하는 것으로만 구성 이것이 non-parametric method로 간주되는 이유 약점 기본 "majority voting" classification의 단점은 class distribution이 편향(skewed)될 때 발생 즉, 더 빈번한 class의 example이 수가 많기 때문에 k k k 이 문제를 극복하는 한 가지 방법은 test point에서 각 k k k Parameter 선택: 최적의 k k k k k k
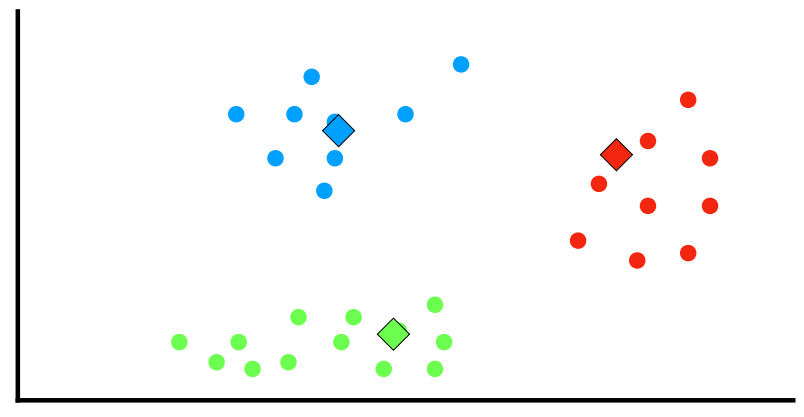
n n n ( x 1 , x 2 , … , x n ) (\mathbf{x}_1,~\mathbf{x}_2,~\dots,~\mathbf{x}_n) ( x 1 , x 2 , … , x n ) x i \mathbf{x}_i x i d d d k k k n n n k ( ≤ n ) k(\le n) k ( ≤ n ) S = { S 1 , S 2 , … , S k } \mathbf{S} = \{S_1,~S_2,~\dots,~S_k\} S = { S 1 , S 2 , … , S k } 공식적으로, 목표는 다음을 찾는 것: argmin S ∑ i = 1 k ∑ x ∈ S i ∥ x − μ i ∥ 2 \underset{\mathbf{S}}{\operatorname{argmin}} \sum_{i=1}^{k} \sum_{\mathbf{x} \in S_i} \left\| \mathbf{x} - \boldsymbol{\mu}_i \right\|^2 S argmin i = 1 ∑ k x ∈ S i ∑ ∥ x − μ i ∥ 2
여기서 μ i \boldsymbol{\mu}_i μ i S i S_i S i k k k 초기 k k k μ 1 ( 1 ) , … , μ k ( 1 ) \boldsymbol{\mu}_1^{(1)},~\dots,~\boldsymbol{\mu}_k^{(1)} μ 1 ( 1 ) , … , μ k ( 1 ) Assignment (Expectation) step: 각 data point를 가장 가까운 평균(least squared Euclidean distance)을 가진 cluster에 할당S i ( t ) = { x p : ∥ x p − μ i ( t ) ∥ 2 ≤ ∥ x p − μ j ( t ) ∥ 2 ∀ j , 1 ≤ j ≤ k } S_i^{(t)} = \{ \mathbf{x}_p : \left\| \mathbf{x}_p - \boldsymbol{\mu}_i^{(t)} \right\|^2 \le \left\| \mathbf{x}_p - \boldsymbol{\mu}_j^{(t)} \right\|^2 \quad \forall j,~1 \le j \le k \} S i ( t ) = { x p : x p − μ i ( t ) 2 ≤ x p − μ j ( t ) 2 ∀ j , 1 ≤ j ≤ k }
여기서 각 x p \mathbf{x}_p x p S ( t ) S^{(t)} S ( t ) Update (Maximization) step: 각 cluster에 할당된 data point들의 (centroid) 평균을 다시 계산μ i ( t + 1 ) = 1 ∣ S i ( t ) ∣ ∑ x p ∈ S i ( t ) x p \boldsymbol{\mu}_i^{(t+1)} = \frac{1}{|S_i^{(t)}|} \sum_{\mathbf{x}_p \in S_i^{(t)}} \mathbf{x}_p μ i ( t + 1 ) = ∣ S i ( t ) ∣ 1 x p ∈ S i ( t ) ∑ x p
할당이 더 이상 변경되지 않을 때 알고리즘은 수렴 그러나 알고리즘이 최적(optimum)을 찾는 것이 보장되지는 않음